AI-powered virtual agents have moved from futuristic concept to everyday reality. From the moment customers land on your website, open your app, or dial your contact center, virtual agents in AI can greet them, solve their problems, and guide them to the right outcome in seconds, providing intelligent assistance for agents along the way. Done right, these tools offer more than just automated responses—they deliver a contact center AI overview and benefits that include improved customer experiences, lower costs, and more productive human teams.
Modern businesses are increasingly relying on cloud-based artificial intelligence platforms for scalable business solutions, which allow companies to deploy intelligent systems without heavy investments in on-site infrastructure. By combining advanced computer technology infrastructure with AI-driven analytics, organizations can streamline operations, enhance cybersecurity, and manage complex workflows more efficiently. In the world of marketing, AI is transforming strategies through automated customer engagement systems, personalized digital marketing campaigns powered by artificial intelligence, and predictive content delivery for online advertising, all designed to connect with audiences in smarter ways.
The financial sector is also embracing AI to improve decision-making and operational efficiency. Solutions like AI-powered financial planning tools, automated risk management systems, predictive financial analytics for smarter investments, and real-time fraud detection using artificial intelligence are helping businesses and consumers alike make faster, more accurate decisions. By integrating these AI capabilities across digital marketing channels, cloud computing platforms, and core financial systems, organizations can create a connected ecosystem where virtual agents not only interact with customers but also leverage data from multiple sources to provide smarter, context-aware support.
In essence, the combination of AI-enabled computer systems, digital marketing intelligence, cloud infrastructure, and financial automation tools creates a foundation where virtual agents act as both front-line problem solvers and strategic enablers, helping businesses stay competitive, reduce operational costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Top 10 AI Contact Center Solutions for Virtual Agents in AI
Virtual agents in AI are transforming the way businesses handle customer interactions, offering intelligent assistance, faster response times, and improved customer satisfaction. Here are the top 10 AI contact center solutions, starting with Bright Pattern.
1. Bright Pattern – AI Contact Center Platform
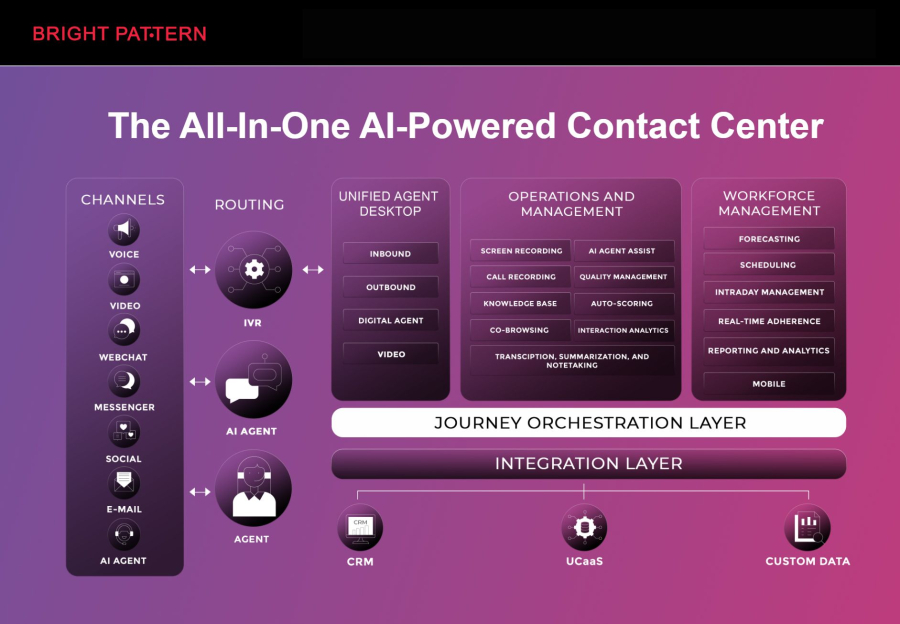
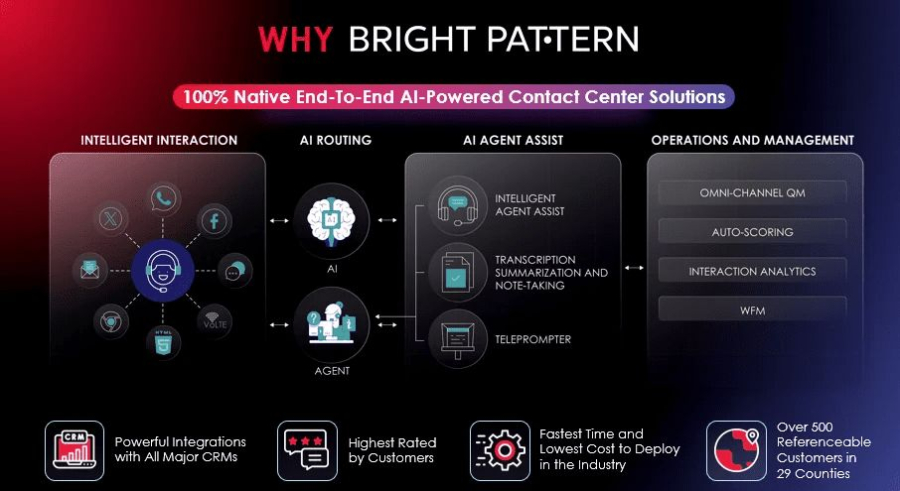
Bright Pattern stands out as a leading provider of AI-powered contact center solutions, helping organizations deploy virtual agents in AI to improve customer service and streamline operations. Its platform integrates cloud-based communication, AI automation, and advanced analytics to create seamless experiences for both customers and agents.
Key Features:
- Omnichannel support across voice, chat, email, SMS, and social media
- AI-powered virtual agents capable of handling routine inquiries and assisting live agents
- Intelligent routing to ensure customers are connected to the right agent or department
- Real-time analytics and performance dashboards to optimize operations
- Cloud-based architecture for scalability, security, and easy integration with existing CRM systems
Bright Pattern’s AI contact center solutions help organizations reduce operational costs, improve agent productivity, and deliver personalized customer experiences across multiple channels. By leveraging AI-driven insights, businesses can continuously improve virtual agent performance and overall customer satisfaction.
2. Genesys Cloud CX
Genesys Cloud CX offers a robust platform for AI contact centers, combining virtual agents in AI with predictive routing, omnichannel messaging, and analytics. It helps businesses automate routine tasks and provide consistent customer experiences.
3. Five9 Intelligent Cloud Contact Center
Five9 delivers AI-powered call center solutions, including virtual agents in AI that handle repetitive inquiries and assist human agents. Its intelligent dialer, CRM integrations, and real-time reporting improve efficiency and customer engagement.
4. Talkdesk CX Cloud
Talkdesk CX Cloud integrates AI virtual agents to streamline contact center operations. It provides real-time analytics, workflow automation, and omnichannel support, enabling businesses to respond faster and smarter to customer needs.
5. NICE inContact CXone
NICE inContact CXone uses AI-driven virtual agents to enhance customer service workflows. Its features include automated call routing, conversational AI, and workforce optimization tools to increase agent productivity.
6. Avaya OneCloud CCaaS
Avaya OneCloud CCaaS offers AI-powered contact center solutions with virtual agents that assist customers across multiple channels. The platform includes speech analytics, automated workflows, and integrations with leading CRM systems.
7. RingCentral Contact Center
RingCentral provides a cloud-based AI contact center platform that leverages virtual agents to handle high-volume interactions efficiently. Features include omnichannel routing, AI-powered insights, and integration with business applications.
8. Cisco Webex Contact Center
Cisco Webex Contact Center integrates AI virtual agents to improve customer interactions and operational efficiency. Its platform supports voice, chat, and social messaging, along with advanced analytics and automation capabilities.
9. Zendesk Suite
Zendesk Suite uses AI-powered virtual agents to manage customer requests and assist human agents with real-time suggestions. The solution provides omnichannel support, automation, and analytics to enhance customer engagement.
10. 8x8 Contact Center
8x8 Contact Center offers AI-enabled virtual agents to improve first-contact resolution and streamline workflows. Its cloud-based platform supports multiple communication channels and provides insights through AI analytics dashboards.
What Is a Virtual Agent in AI?
Avirtual agentis an AI-powered software entity that can interact with people using natural language, understand their intent, and take actions on their behalf. It is often called avirtual assistant,intelligent agent, orconversational agent.
Unlike simple chatbots that rely only on static rules, modern virtual agents use a combination of:
- Natural language processing (NLP)to understand what users say or type.
- Dialogue managementto keep track of context and carry on multi-step conversations.
- Machine learningto improve over time based on real interactions.
- Backend integrationsto perform real actions, such as updating records or processing requests.
The result is an assistant that can handle many of the same tasks a human agent would, but instantly, consistently, and at massive scale.
Key Types of AI Virtual Agents
Virtual agents can appear in different forms depending on the channel, user interface, and purpose. The underlying intelligence can be similar, but the experience is adapted to the context.
1. Text-Based Virtual Agents (Chat Assistants)
These are the most common and visible type of virtual agent today. They interact via text in channels such as:
- Website chat widgets.
- Mobile apps.
- Messaging platforms and SMS.
- In-product assistants embedded into software tools.
They can answer questions, guide users through forms, help them complete tasks, and hand off to human agents when needed.
2. Voice-Based Virtual Agents (Voicebots)
Voice-based agents interact via spoken language. They power experiences such as:
- Smart speakers and home assistants.
- Interactive voice response (IVR) systems in contact centers.
- In-car assistants and voice-enabled devices.
These agents rely on speech recognition to convert audio into text, then apply the same AI techniques as text-based assistants.
3. Multimodal Virtual Agents
Multimodal agents combine multiple input and output modes, such as text, voice, and even visual elements. For example, an assistant on a smartphone might:
- Listen to your spoken request.
- Show supporting information on the screen.
- Guide you through steps with both text and voice prompts.
These experiences feel more natural and adaptive, especially on devices with rich displays.
4. Specialized Domain Agents
Some virtual agents are built to operate in a specific domain with deeper expertise, such as:
- Customer service and technical support.
- Banking and financial advice.
- Healthcare triage and patient guidance.
- HR and employee self-service.
Because they are tailored to a defined set of tasks and terminology, these agents can be highly effective and accurate within their domain.
How AI Virtual Agents Work
While implementations vary, most modern virtual agents share a similar core architecture. Understanding these components helps you design better experiences and evaluate solutions more effectively.
1. Input Processing
The first step is capturing what the user says or types:
- Text inputis processed directly.
- Voice inputis converted to text using automatic speech recognition.
Once in text form, the conversation can move through the rest of the pipeline.
2. Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
NLUmodels analyze the text to understand the user's intent and extract key details. This often includes:
- Intent classification(for example, "reset password", "check order status", "update address").
- Entity extraction(for example, names, dates, account IDs, product names).
- Sentiment detectionto gauge user frustration or satisfaction.
Modern NLU systems can handle a wide variety of phrasing, spelling errors, and informal language, making interactions more natural.
3. Dialogue Management
Thedialogue managerdecides how the virtual agent should respond and what to do next. It maintains the context of the conversation, including:
- What the user has already told the agent.
- Which steps in a process have been completed.
- Which clarifying questions still need to be asked.
Dialogue management can be rule-based, AI-driven, or a hybrid of both. Hybrid approaches allow you to enforce business rules while still benefiting from flexible, natural conversations.
4. Business Logic and Integrations
To be truly useful, virtual agents must connect with your existing systems and data. Typical integrations include:
- Customer relationship management (CRM) platforms.
- Order management and billing systems.
- Knowledge bases and documentation tools.
- Internal APIs and databases.
This is where virtual agents move from simply answering questions to actually taking action, such as placing orders, updating profiles, or creating support tickets.
5. Natural Language Generation (NLG)
Once the agent knows what to say or do, it usesnatural language generationto craft a response. This can range from:
- Template-based replies that ensure consistent wording and compliance.
- AI-generated text that adapts tone and detail to the user's needs.
Responses can be optimized over time to be clearer, shorter, or more helpful based on interaction data.
6. Continuous Learning and Improvement
The most powerful virtual agents improve continuously by learning from past conversations. This can involve:
- Identifying new intents or topics that users frequently ask about.
- Refining training data to reduce misclassifications.
- Analyzing where conversations break down and adjusting flows.
- Testing variations of responses to see which ones resolve issues fastest.
This feedback loop turns each interaction into an opportunity to make the agent smarter and more valuable.
Major Benefits of AI Virtual Agents for Organizations
When implemented strategically, virtual agents deliver benefits that compound over time. The gains are both operational and experiential.
1. 24/7 Availability Without Added Headcount
Virtual agents never sleep, go on vacation, or wait on hold. They can provide instant support at any time of day, in any time zone. This is especially powerful if you support global customers or see high demand outside traditional business hours.
2. Faster Response Times and Reduced Wait Times
Customers and employees increasingly expect answers in seconds, not minutes. Virtual agents can respond instantly to common questions, dramatically cutting queue times and reducing frustration.
This speed is particularly valuable for:
- High-volume, repetitive inquiries.
- Time-sensitive requests, such as password resets or order tracking.
- First-contact resolution of simple issues.
3. Lower Operational Costs
By automating routine tasks, virtual agents help you handle more interactions without scaling headcount at the same rate. This does not replace human teams; instead, it shifts their focus to high-value work where human judgment and empathy matter most.
Cost savings often come from:
- Deflecting calls and tickets that do not require human expertise.
- Shortening average handling time by pre-collecting information.
- Reducing training and ramp-up time for new staff.
4. Consistent, Compliant Answers
Virtual agents deliver the same accurate, up-to-date information every time, based on centrally managed content and business rules. This is particularly valuable in regulated industries such as finance and healthcare, where consistency and compliance are critical.
5. Rich Data and Actionable Insights
Every interaction with a virtual agent generates structured data about what users ask, how they phrase questions, and where they encounter roadblocks. This data can reveal:
- Gaps in your knowledge base or documentation.
- Product or service issues that drive contact volume.
- Opportunities to streamline forms, processes, or onboarding flows.
Captured correctly, these insights feed continuous improvement across customer experience, product design, and operations.
6. Enhanced Employee Productivity
Virtual agents are not only for customers. Internal assistants can help employees:
- Find HR, IT, or policy information quickly.
- Automate repetitive administrative tasks.
- Navigate complex internal tools through conversational guidance.
This reduces time spent on low-value tasks and frees teams to focus on strategic, creative, or relationship-driven work.
High-Impact Use Cases for AI Virtual Agents
Organizations across industries are deploying virtual agents in creative ways. Here are some of the most impactful scenarios.
Customer Support and Service
- Answering common questions about orders, billing, and account settings.
- Guiding troubleshooting steps for technical products.
- Resetting passwords and managing basic account security flows.
- Providing status updates on shipments, appointments, or service requests.
Sales and Lead Generation
- Engaging website visitors proactively and qualifying leads.
- Recommending products or plans based on user needs.
- Booking demos, appointments, or consultations automatically.
- Nurturing leads with timely, conversational follow-ups.
Onboarding and Customer Success
- Walking new customers through setup and configuration steps.
- Offering tips, tutorials, and best practices within your product.
- Answering how-to questions in context, without leaving the page or app.
HR and Employee Self-Service
- Answering questions about benefits, payroll, and company policies.
- Helping employees request time off, update details, or access forms.
- Assisting with IT support for common issues like access and configuration.
Banking, Insurance, and Financial Services
- Explaining account features, fees, and eligibility criteria.
- Guiding customers through claims, applications, or loan pre-qualification.
- Providing personalized insights, such as spending overviews or alerts.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Helping patients schedule or reschedule appointments.
- Answering questions about clinic hours, coverage, or preparation guidelines.
- Offering general wellness guidance and triage within approved boundaries.
Comparing Virtual Agents to Traditional Chatbots
Virtual agents are often contrasted with older, rule-based chatbots. While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there are important differences in capabilities and outcomes.
Aspect | Traditional Chatbot | AI Virtual Agent |
Understanding | Keyword or menu-based; struggles with natural language. | Uses NLP to understand intent and entities in free-form text or speech. |
Conversation | Linear, script-based flows; limited context awareness. | Contextual, multi-turn dialogues; can handle interruptions and clarifications. |
Learning | Static flows; manual updates required. | Improves over time using real interaction data and ML models. |
Integration | Often limited or one-way connections. | Deep integration with business systems for end-to-end task completion. |
Business Impact | Helpful for basic FAQs. | Drives significant automation, cost savings, and experience improvements. |
Designing a Successful Virtual Agent Strategy
Launching a virtual agent is more than a technical project. The most successful deployments start with clear goals, focused scope, and thoughtful experience design.
1. Define Clear Objectives
Before selecting technology, identify what success looks like. Common objectives include:
- Reducing live chat or call volume by a specific percentage.
- Improving first-contact resolution rates for common issues.
- Shortening onboarding time for new customers.
- Providing 24/7 support without adding overnight staffing.
Clear goals make it easier to prioritize features, design flows, and measure impact.
2. Start with High-Value, High-Volume Use Cases
Instead of trying to automate everything at once, focus the first phase on tasks that are:
- Frequent(many customers ask about them).
- Structured(they follow clear steps and rules).
- Impactful(they affect satisfaction, cost, or speed).
This approach helps you deliver visible wins quickly while building internal confidence.
3. Map End-to-End Conversation Flows
Design conversations like user journeys, not just scripts. Consider:
- Different ways users might phrase the same intent.
- Questions the agent needs to ask to complete a task.
- Fallback paths when the agent is uncertain.
- Seamless handoffs to human agents when needed.
Visual flow diagrams can help stakeholders understand and refine the experience.
4. Plan for Human Handoffs
Even the best virtual agents will not handle every scenario. Design a positive experience when the agent needs help:
- Make it easy for users to request a human agent at any time.
- Transfer context (conversation history, collected details) so customers do not repeat themselves.
- Set expectations about wait times and next steps.
Blending AI with human expertise creates trust and ensures complex situations are resolved effectively.
5. Align Tone and Personality with Your Brand
Virtual agents represent your organization in every interaction. Define a consistent voice and personality that matches your brand and audience expectations, including:
- Formality level (casual vs. professional).
- Use of humor or small talk, when appropriate.
- Empathy guidelines for sensitive interactions, such as complaints or health issues.
A thoughtful voice and tone guide helps keep responses friendly, helpful, and on-brand.
Measuring the Success of Your Virtual Agent
To unlock ongoing value, treat your virtual agent like a product, not a one-time project. Define metrics, track performance, and iterate continuously.
Core Performance Metrics
- Containment rate: The percentage of conversations resolved by the virtual agent without human intervention.
- Deflection rate: Reduction in live channel volume (calls, chats, tickets) after deployment.
- First-contact resolution (FCR): How often the initial interaction solves the issue.
- Average handling time (AHT): Time spent resolving issues, both within the agent and when handed to humans.
- Customer satisfaction (CSAT or similar)after interactions with the virtual agent.
Quality and Experience Metrics
- Fallback rate: How often the agent says it does not understand.
- Escalation reasons: Why conversations are handed to humans.
- Drop-off points: Where users abandon the conversation.
These insights highlight where to improve training data, conversation flows, or content.
Best Practices for Long-Term Success
Organizations that see the greatest benefit from virtual agents treat them as evolving capabilities. A few best practices stand out.
1. Invest in High-Quality Training Data
The accuracy of your virtual agent depends heavily on the examples it learns from. Collect real customer queries, including different phrasings, typos, and languages where relevant. Continuously refine and expand this dataset to reduce misunderstanding.
2. Keep Knowledge and Content Fresh
Ensure the content behind your virtual agent stays up to date by:
- Establishing ownership for each topic area.
- Reviewing content when products, policies, or pricing change.
- Using analytics to identify high-impact articles or flows to optimize first.
3. Prioritize Security and Privacy
Virtual agents frequently work with personal or sensitive data. Collaborate with security and compliance teams to:
- Define what information the agent can and cannot access.
- Implement strong authentication where needed.
- Ensure data is handled in line with your privacy policies and regulations.
4. Communicate Clearly with Users
Transparency builds trust. Make it clear that users are interacting with a virtual agent, and set expectations about what it can and cannot do. Offer guidance, such as example questions, to help users get started.
5. Iterate with a Cross-Functional Team
The most effective virtual agent programs bring together expertise from:
- Support and service teams, who understand customer needs and pain points.
- Product and operations teams, who know processes and systems.
- Data and AI specialists, who can tune models and interpret analytics.
- Compliance and security stakeholders, who ensure safe deployment.
This collaborative approach keeps the virtual agent aligned with real-world goals and constraints.
The Future of AI Virtual Agents
Virtual agents are evolving quickly as AI capabilities advance. Several trends are shaping the next generation of intelligent assistants.
More Human-Like Conversations
Improvements in large language models and conversational AI are making dialogues feel more natural, flexible, and context-aware. Agents can better handle:
- Open-ended questions.
- Longer, more complex requests.
- Multi-step tasks that span different systems.
Deeper Personalization
As integration with customer data improves, virtual agents can personalize experiences based on:
- Past interactions and preferences.
- Account type, lifecycle stage, or purchase history.
- Real-time context, such as current location or device.
This personalization can increase relevance, speed up resolution, and boost satisfaction.
Expanded Roles Across the Organization
Virtual agents are expanding beyond support into every corner of the business. Examples include:
- Sales assistants that help teams prepare for meetings or craft proposals.
- Operations helpers that monitor systems and suggest improvements.
- Training companions that guide new employees through learning paths.
Responsible and Trustworthy AI
As virtual agents take on more critical roles, organizations are emphasizing responsible AI practices. This includes:
- Clear governance over how models are trained and updated.
- Bias monitoring and mitigation.
- Human oversight for sensitive decisions.
These efforts help maintain user trust while unlocking the full potential of intelligent automation.
Getting Started with AI Virtual Agents
Launching your first or next virtual agent initiative is an opportunity to transform how your organization serves customers and employees. To move forward confidently:
- Clarify your top three business objectives and success metrics.
- Choose a focused, high-value use case for your initial rollout.
- Engage stakeholders across support, product, IT, and compliance early.
- Design conversations from the user's perspective, with clear handoffs.
- Set up regular review cycles to tune performance and expand scope.
With the right strategy and ongoing investment, AI virtual agents become a powerful extension of your team, delivering faster, more personalized, and more efficient experiences at scale.
The organizations that embrace virtual agents today are not just cutting costs; they are laying the foundation for smarter, more responsive, and more human-centered digital experiences for years to come.
